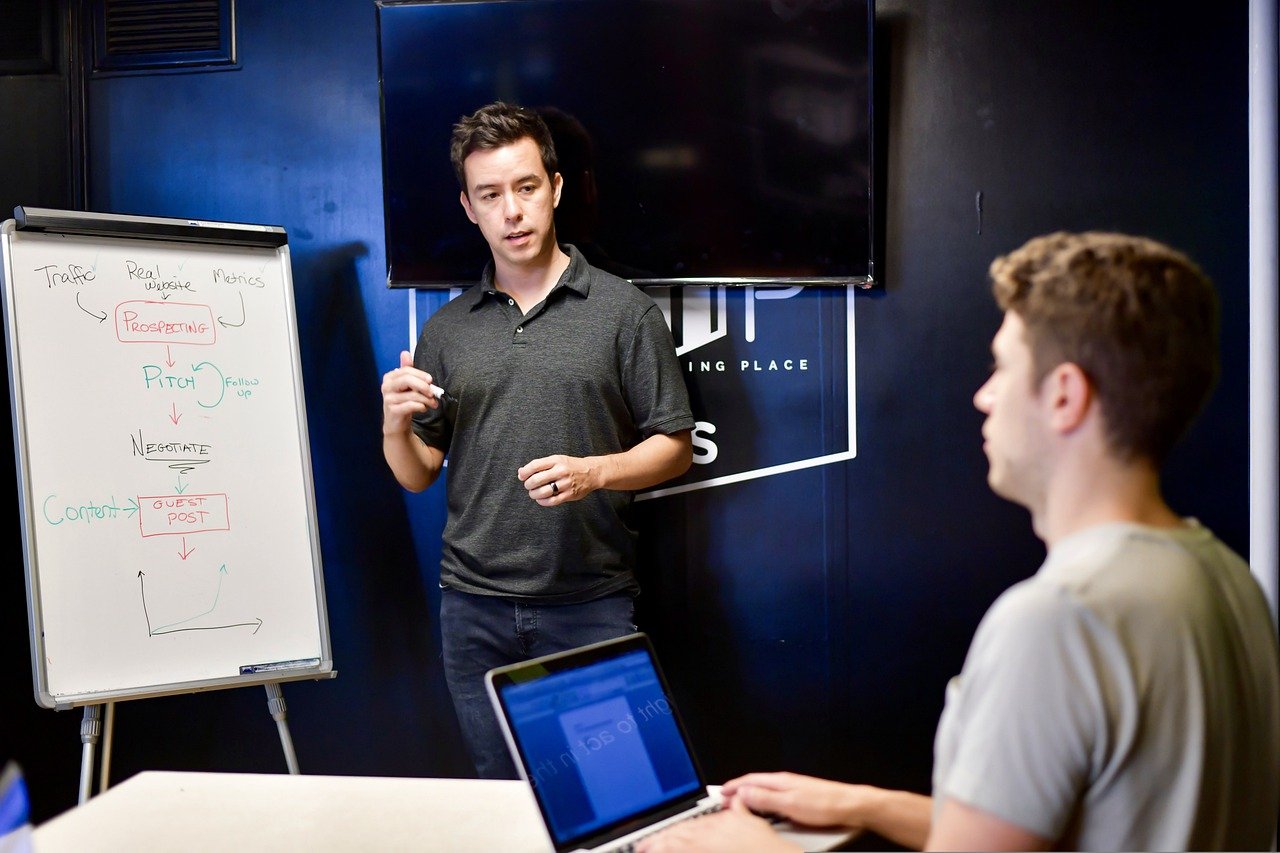
Previously, the search engine was unable to reach consumer intent. Words in a query string were linking to words on results pages. The results were being shown to the user. This client’s intent behind these words was not understood. Now, the advanced Internet technology allows the Google SERPS to improve and become much more modern. SERP, Search Engine Result Page is always improved for a better user experience. In this article, we will look at the interpretation of modern SERPs to achieve better ranking.

The Aims of the SERPs
Today, the goal of search engines is to provide the best possible search experience for users. It includes identifying SERPs on the expected intent of the customer. Over time, a lot of attention has been paid to understanding customer intent and why different users with numerous goals use the same words in their queries. Also, Google not only wants to deliver search results but also deliver results instantly. It means that consumers get all the information that meets their needs in the shortest possible time. It has implications for the structure of your SERP layout and your position on search engine results pages.
Aside from that, rankings are crucial for brands and businesses. Higher rankings mean more leads and organic traffic. Ultimately, this means more revenue and more profit for the company. However, it doesn’t mean being at the top of the page. Instead, it can be beneficial for your brand to be at the top of the search results or be included in the snippet area.
The Algorithm of the PageRank
 Google’s algorithm was based on “PageRank.” In simple terms, it means that the more people who agree with a page, the higher its credibility. However, the search algorithms had come a long way from the day the top ten sites were listed as links. The personalized search engine was then published which the factors include user’s search history, IP addresses, location, and social media activity.
Google’s algorithm was based on “PageRank.” In simple terms, it means that the more people who agree with a page, the higher its credibility. However, the search algorithms had come a long way from the day the top ten sites were listed as links. The personalized search engine was then published which the factors include user’s search history, IP addresses, location, and social media activity.
Vital Universal Search Algorithm Updates of Google
Nowadays, Google integrated its vertical and neighborhood searches for information, video, images, and graphics into a format called Universal Search. In 2010, further algorithm updates were made through Google ‘Caffine’. In 2012, with the introduction of the Penguin update, unnatural links were combated. Google is constantly experimenting with the number of results, new results, and ad formats. The introduction of snippets has once again changed the way searches are done.
Conclusion
Google is not a fixed set of calculations. Algorithms are always invisible to understand the elegance behind the set of phrases in a query. Google constantly changes and maintains and introduces updates regularly. Also, almost daily adjustments are made to the search process, often substantial changes. Hence, neither the SERPs nor the search queries will be the same. Note that you can’t plan to rank variety every time, but you need to.